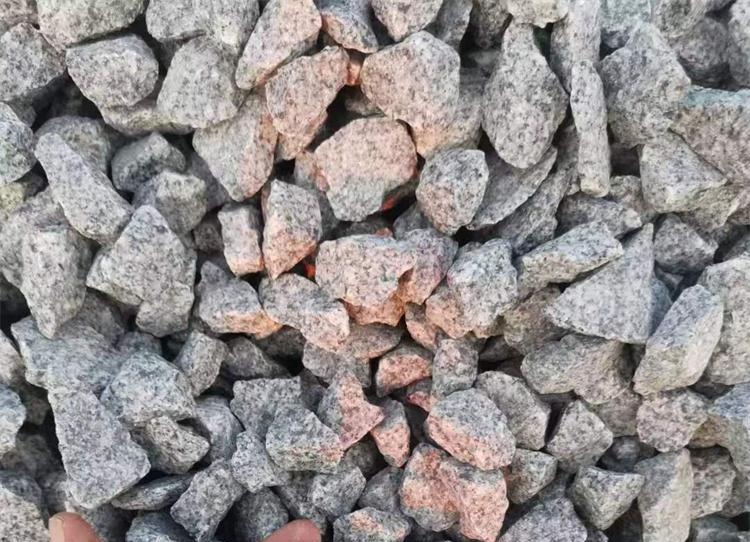
The construction of roads and railways relies heavily on high-quality basalt — a durable mixture of coarse aggregates that forms the foundational layer for long-term structural stability and optimal load-bearing performance. Traditionally, basalt is processed in centralized fixed crushing facilities, often requiring extensive transportation of raw materials and finished aggregates. While effective in some contexts, this model increasingly proves inefficient and costly, especially in geographically dispersed or time-sensitive projects.
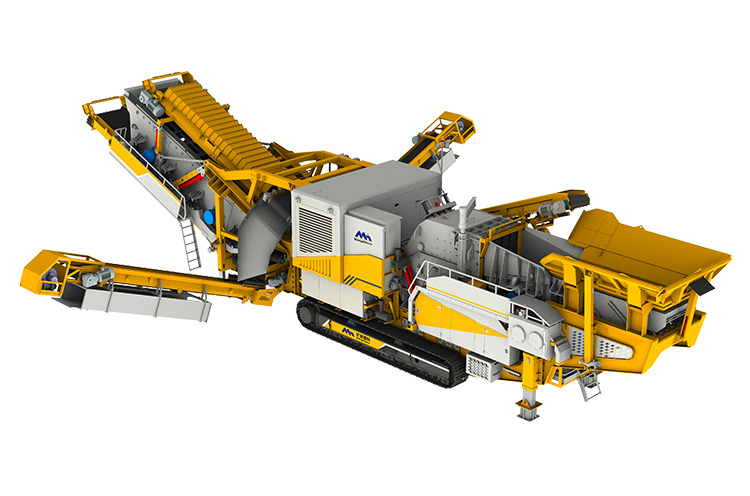
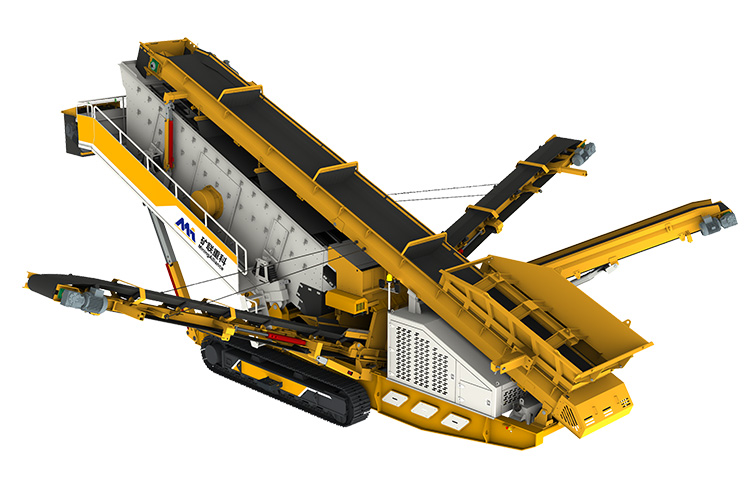
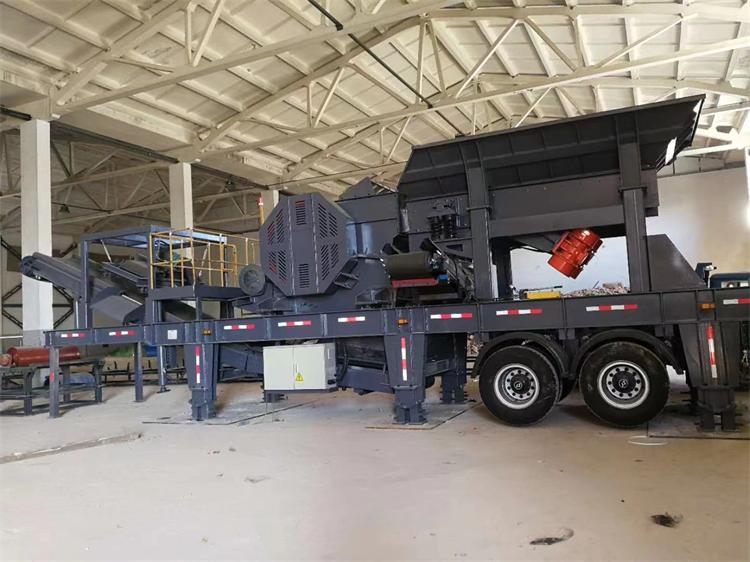
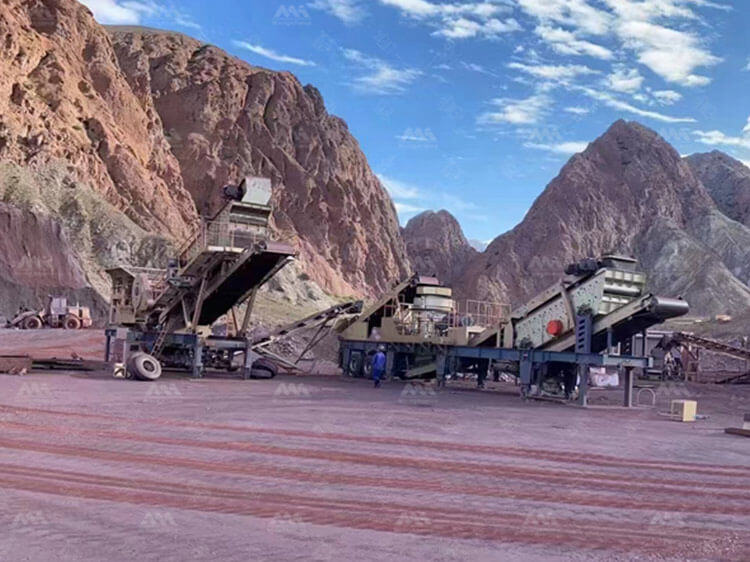
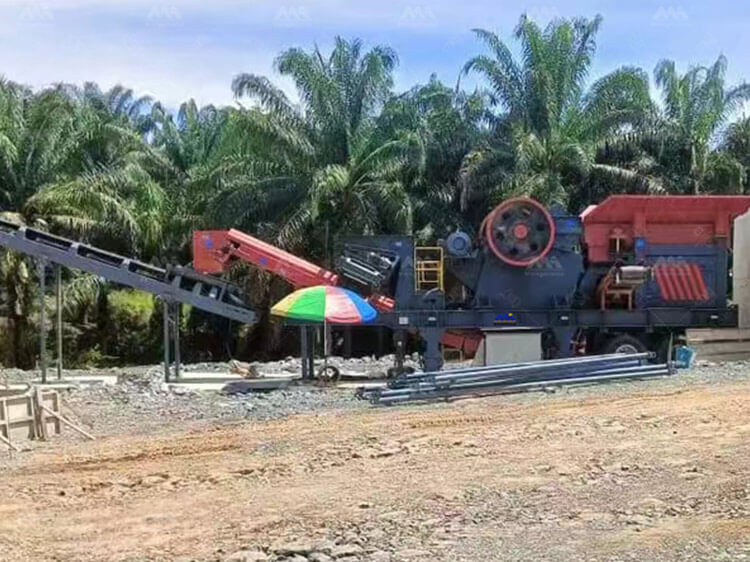
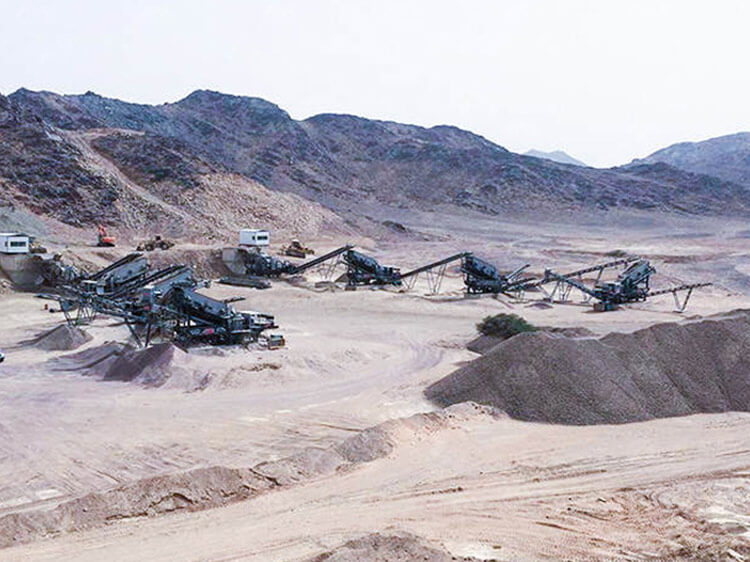
To address these limitations, the industry has witnessed a significant shift toward mobile crushing and screening stations. These all-in-one systems offer unmatched flexibility and cost-efficiency by taking the crushing operation directly to the job site. Whether deployed in remote quarries, highway expansion corridors, or railway construction zones, mobile units drastically reduce logistics costs and operational delays.
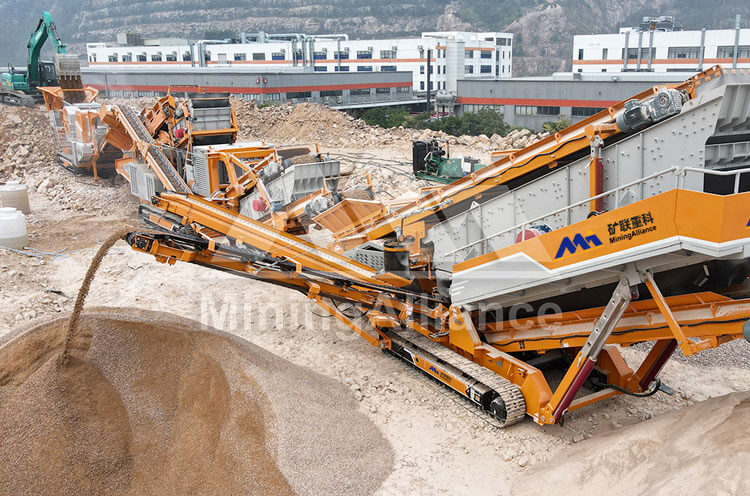

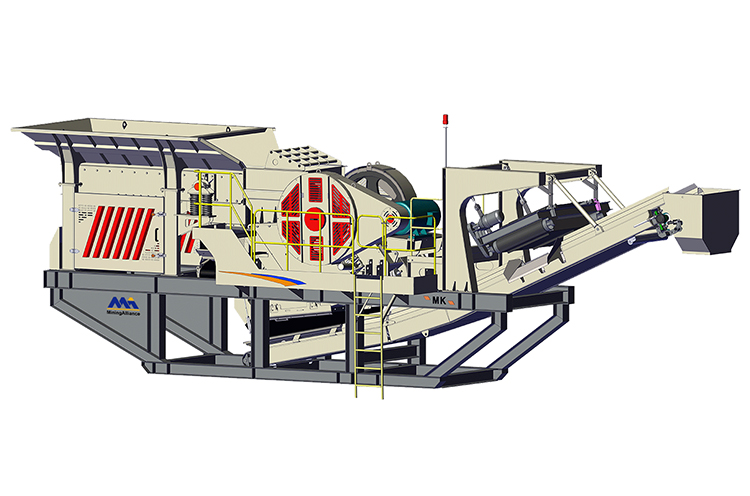
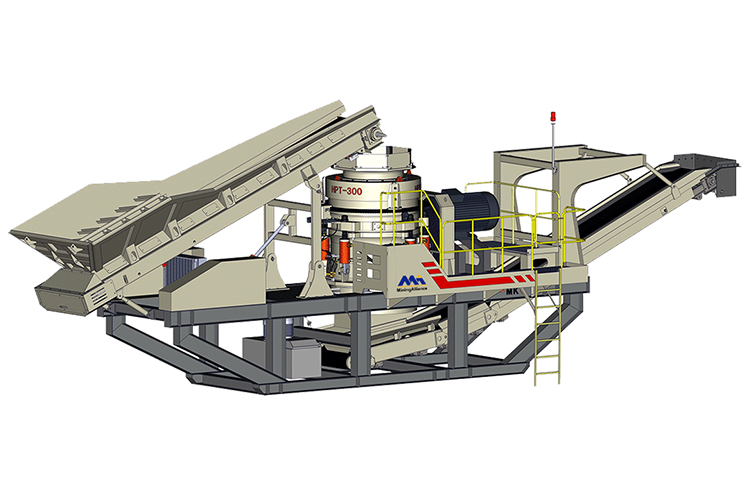
Typically, a mobile basalt production line is composed of a jaw crusher for primary crushing, followed by a cone crusher for secondary or tertiary stages, depending on the hardness and fragmentation requirements of the material. Given that granite — often used as basalt — has a Mohs hardness above 6, the robust design of mobile jaw crushers and high-performance cone crushers is essential to ensure reliable output without excessive wear.
In addition to crushers, modern mobile units are equipped with vibrating screens, which enable real-time material classification and separation. This capability allows contractors to produce multiple fractions (e.g., 31.5mm, 25mm, 16mm) simultaneously, reducing the need for secondary screening plants. Integrated conveyors, hydraulic systems, and advanced PLC controls further automate the process, enhancing output consistency and minimizing manual intervention.
Environmental benefits are also notable. Mobile plants can be outfitted with dust suppression systems, noise insulation, and energy-efficient motors, aligning with increasingly strict sustainability regulations in large infrastructure projects.